Sleep is crucial for children's growth and development, both physically and mentally. However, various factors can disrupt their sleep patterns, one of the most concerning being Sleep Disordered Breathing (SDB). SDB encompasses a spectrum of breathing problems during sleep, ranging from snoring to obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and effective solutions for managing Sleep Disordered Breathing in children.
Understanding Sleep Disordered Breathing:
Sleep Disordered Breathing refers to a group of disorders characterized by abnormalities in breathing during sleep. While snoring is the most common manifestation, it can progress to more severe conditions like obstructive sleep apnea, where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep.
Causes of Sleep Disordered Breathing in Children:
- Obstructive Factors: The most common cause of SDB in children is the obstruction of the upper airway during sleep. This obstruction can result from enlarged tonsils and adenoids, which are prevalent in children.
- Structural Abnormalities: Certain structural abnormalities, such as a small jaw or large tongue, can contribute to airway obstruction during sleep.
- Obesity: Childhood obesity has become a significant risk factor for SDB. Excess fat deposits around the neck can exert pressure on the airway, leading to breathing difficulties during sleep.
- Neuromuscular Disorders: Conditions like cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy can affect the muscles responsible for maintaining an open airway during sleep, increasing the risk of SDB.
- Family History: Genetic predispositions can also play a role in the development of Sleep Disordered Breathing in children. If a child's parents have a history of SDB, the likelihood of the child experiencing similar issues increases.
Symptoms of Sleep Disordered Breathing:
Recognizing the signs of Sleep Disordered Breathing is crucial for early intervention and management. Common symptoms include:
- Loud Snoring: Persistent loud snoring, especially accompanied by gasping or choking sounds during sleep, is often indicative of SDB.
- Daytime Sleepiness: Children with SDB may exhibit excessive daytime sleepiness, which can manifest as difficulty waking up in the morning, frequent napping, or poor concentration during the day.
- Behavioral Issues: SDB can impact a child's behavior, leading to irritability, mood swings, and difficulty focusing in school.
- Breathing Pauses: Observing episodes of breathing pauses during sleep is a significant red flag for obstructive sleep apnea.
Diagnosis of Sleep Disordered Breathing:
Proper diagnosis of Sleep Disordered Breathing in children typically involves a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examination, and diagnostic tests.
- Medical History: The healthcare provider will inquire about the child's sleep habits, snoring frequency, and any daytime symptoms.
- Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination, including an assessment of the airway and examination of the tonsils and adenoids, is crucial for identifying any anatomical abnormalities.
- Sleep Study (Polysomnography): Polysomnography is the gold standard diagnostic test for evaluating sleep disorders. It records various parameters during sleep, including breathing patterns, oxygen levels, and brain activity.
Solutions for Managing Sleep Disordered Breathing:
The management of Sleep Disordered Breathing in children often requires a multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals from various specialties.
- Adenotonsillectomy: Surgical removal of the tonsils and adenoids (adenotonsillectomy) is often the first-line treatment for children with obstructive sleep apnea due to enlarged tonsils and adenoids.
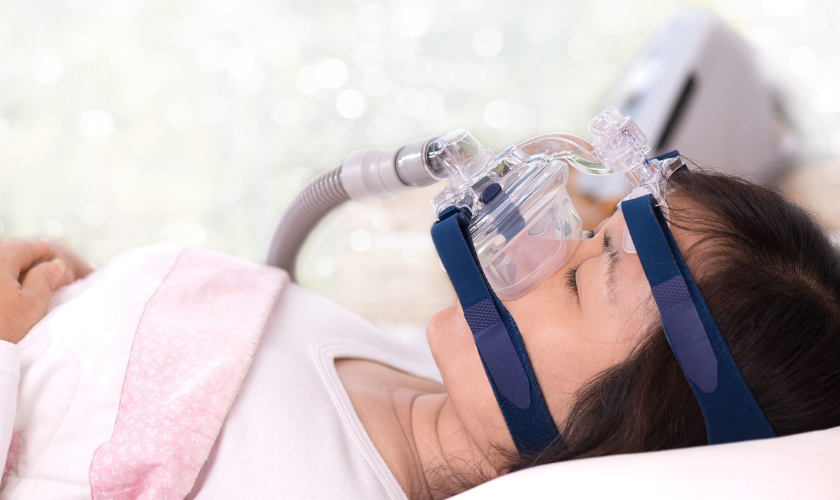
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Therapy: CPAP therapy involves wearing a mask connected to a machine that delivers a continuous flow of air pressure, keeping the airway open during sleep.
- Weight Management: For children who are overweight or obese, weight management through healthy diet and regular exercise can help alleviate SDB symptoms.
- Orthodontic Treatment: In cases where structural abnormalities contribute to airway obstruction, orthodontic interventions such as palate expanders or orthognathic surgery may be recommended.
- Positional Therapy: Encouraging children to sleep in a specific position, such as on their side, can sometimes reduce the severity of SDB symptoms.
- Behavioral Modifications: Implementing behavioral changes such as establishing a consistent bedtime routine and creating a conducive sleep environment can improve sleep quality and reduce SDB symptoms.
Sleep Disordered Breathing can have significant implications for children's health and well-being if left untreated. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available solutions for managing SDB, parents and healthcare providers can work together to ensure early intervention and effective treatment. Through a combination of lifestyle modifications, surgical interventions, and therapeutic approaches, children with Sleep Disordered Breathing can experience improved sleep quality and overall health outcomes. Prioritizing healthy sleep habits and seeking timely medical intervention are essential steps in promoting optimal sleep health for children.
